Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling: An Emerging Tool in Research
What is partial least squares structural equation modeling?
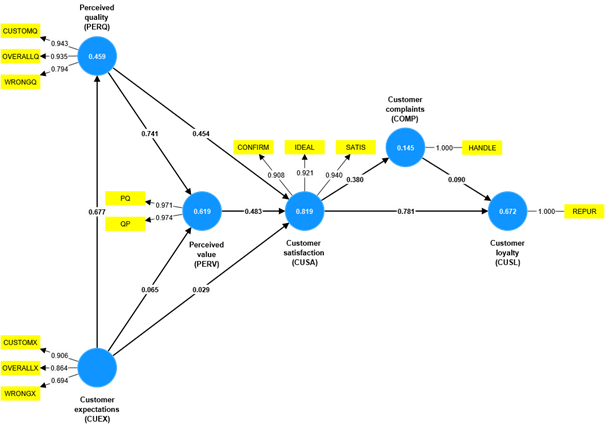
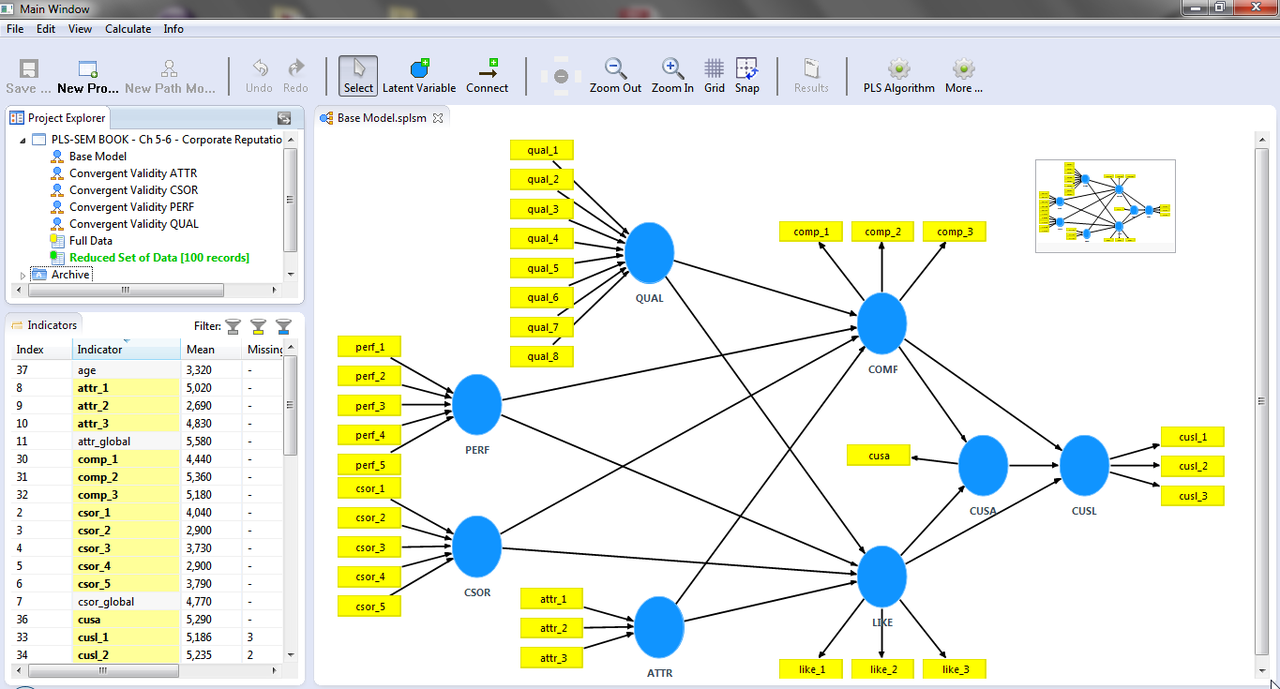
Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) has gained attention in research and practice across various disciplines such as management, marketing, information systems, medicine, engineering, psychology, political and environmental sciences. PLS-SEM enables researchers to model and estimate complex cause-effects relationship models with both latent (graphically represented as circles) and observed variables (graphically represented as rectangles).
The latent variables embody unobserved (i.e., not directly measurable) phenomena such as perceptions, attitudes, and intentions.
The observed variables (e.g., responses on a questionnaire or secondary data) are used to represent the latent variables in a statistical model.
PLS-SEM estimates the relationships between the latent variables (i.e., their strengths) and determines how well the model explains the target constructs of interest.
The main reasons for the popularity of PLS-SEM are its capability to estimate very complex models and its relaxed data requirements. The most popular applications are the estimation of technology acceptance models (TAM) and American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) models. Each of these models has been published in thousands of different of studies.
PLS-SEM also increased the analytical demands connected with the method. Hence, recent research presented numerous methodological extensions to provide researchers and practitioners with a broad portfolio of technical options to meet their analytical goals. These extensions include, for example, the importance-performance map, mediation, moderation, multi group, latent class segmentation, and predictive analyses
Learn more about partial least squares structural equation modeling
To get to know the PLS-SEM method, the third edition of A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) by Joe Hair, Thomas Hult, Christian Ringle, and Marko Sarstedt, and the second edition of Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling by Hair, Sarstedt, Ringle, and Siegfried Gudergan, are practical guides that provide researchers with a shortcut to fully understand and competently use the rapidly emerging multivariate PLS-SEM technique.
While the primer offers an introduction to fundamental topics such as establishing, estimating and evaluating PLS path models and some additional topics such as mediation and moderation, the book on advanced issues fully focuses on complementary analyses such as testing nonlinear relationships, latent class segmentation, multigroup analyses, measurement invariance assessment, and higher-order models. Featuring the latest research, examples analyzed with the SmartPLS 4 software, and expanded discussions throughout, these two books are designed to be easily understood by those want to exploit the analytical opportunities of PLS-SEM in research and practice. There is also an associated website for both books. Use the code COMMUNIT24 for a 25% discount when you order books from Sage, good until December 31, 2024.
Open access journal articles about partial least squares structural equation modeling
Becker, J.-M./ Cheah, J.H./ Gholamzade, R./ Ringle, C.M./ Sarstedt, M.: PLS-SEM’s Most Wanted Guidance, International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, Volume 35 (2023), Issue 1, pp. 321-346.
Cook, D.R./ Forzani, L. On the Role of Partial Least Squares in Path Analysis for the Social Sciences. Journal of Business Research, Volume 167 (2023), p. 114132.
Guenther, P./ Guenther, M./ Ringle, C. M./ Zaefarian, G./ Cartwright, S.: Improving PLS-SEM Use for Business Marketing Research. Industrial Marketing Management, Vol. 111 (2023), pp. 127-142.
Morgeson, F.V./ Hult, G.T.M./ Sharma, U./ Fornell, C.: The American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI): A Sample Dataset and Description. Data in Brief, Volume 48 (2023), p. 109123.
Ringle, C.M./ Sarstedt, M./ Sinkovics, N./ Sinkovics, R.R.: A Perspective on Using Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modelling in Data Articles, Data in Brief, Vol. 48 (2023), p. 109074.
Sarstedt, M./ Ringle, C.M./ Iuklanov, D.: Antecedents and Consequences of Corporate Reputation: A Dataset, Data in Brief, Vol. 48 (2023), p. 109079.
More Sage Research Methods Community posts about quantitative and computational methods
As part of our ongoing commitment to delivering high-quality online learning, we are excited to announce a series of updates to our Sage Campus courses! These enhancements are designed to support academic success by providing practical resources and empowering learners at every stage of their academic journey.
Last month Sage hosted an exclusive webinar with the JASP founder, Eric-Jan Wagenmakers, and fellow JASP creator Johnny van Doorn. Based at the University of Amsterdam, these renowned experts introduced the world of teaching statistics using JASP.
Sample a selection of the most helpful methods videos and guides published in 2024 on the Sage Research Methods online platform with free access.
This blog is the seventh, and penultimate post, in a follow-on to our 2021 “The future of computational social science is Black” series, about a Summer Institute in Computational Social Science organized by Howard University and Mathematica. It continues to bring the power of computational social science to the issues of systemic racism and inequality in America. This marks the third iteration of the successful SICSS model being hosted by a Historically Black College or University.
This blog post is the sixth of eight in a follow-on to our 2021 “The future of computational social science is Black” series, about a Summer Institute in Computational Social Science organized by Howard University and Mathematica. It continues to bring the power of computational social science to the issues of systemic racism and inequality in America. This marks the third iteration of the successful SICSS model being hosted by a Historically Black College or University.
Latanya Sweeney, scholar of technology science, Daniel Paul Professor of the Practice of Government and Technology at the Harvard Kennedy School and in the Harvard Faculty of Arts and Sciences, and director and founder of the Public Interest Tech Lab, delivered the keynote address for SICSS-Howard/Mathematica 2023.
This blog post is the fifth of eight in a follow-on to our 2021 “The future of computational social science is Black” series, about a Summer Institute in Computational Social Science organized by Howard University and Mathematica. It continues to bring the power of computational social science to the issues of systemic racism and inequality in America. This marks the third iteration of the successful SICSS model being hosted by a Historically Black College or University.
This blog post is the fourth of eight in a follow-on to our 2021 “The future of computational social science is Black” series, about a Summer Institute in Computational Social Science organized by Howard University and Mathematica. It continues to bring the power of computational social science to the issues of systemic racism and inequality in America. This marks the third iteration of the successful SICSS model being hosted by a Historically Black College or University.
This blog post is the third of eight in a follow-on to our 2021 “The future of computational social science is Black” series, about a Summer Institute in Computational Social Science organized by Howard University and Mathematica. It continues to bring the power of computational social science to the issues of systemic racism and inequality in America. This marks the third iteration of the successful SICSS model being hosted by a Historically Black College or University.
This blog post is the second of eight in a follow-on to our 2021 “The future of computational social science is Black” series, about a Summer Institute in Computational Social Science organized by Howard University and Mathematica. It continues to bring the power of computational social science to the issues of systemic racism and inequality in America. This marks the third iteration of the successful SICSS model being hosted by a Historically Black College or University.
This blog post is the first of eight in a follow-on to our “The future of computational social science is Black” series, about a Summer Institute in Computational Social Science organized by Howard University and Mathematica. It continues to bring the power of computational social science to the issues of systemic racism and inequality in America. This marks the third iteration of the successful SICSS model being hosted by a Historically Black College or University.
Learn about options available in the dynamic landscape of emerging methodological extensions in the PLS-SEM field is the necessary condition analysis (NCA).
How can you use data science in social science research? Find an interview with the Oxford Internet Institute’s Dr. Bernie Hogan and lots of useful resources in this post.
Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) enables researchers to model and estimate complex cause-effects relationship models
Find tips to help you share your research and numerical findings.
Dr. Stephen Gorard defines and explains randomness in a research context.
Mentor in Residence Stephen Gorard explains how researchers can think about predicting results.
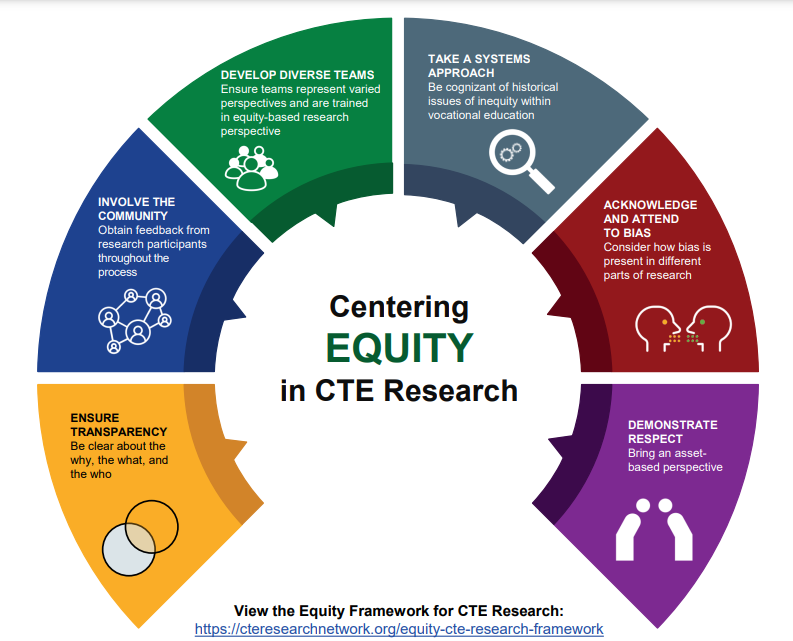
The Career and Technical Education (CTE) Equity Framework approach draws high-level insights from this body of work to inform equity in data analysis that can apply to groups of people who may face systemic barriers to CTE participation. Learn more in this two-part post!
The Career and Technical Education (CTE) Equity Framework approach draws high-level insights from this body of work to inform equity in data analysis that can apply to groups of people who may face systemic barriers to CTE participation. This is part 2, find the link to part 1 and previous posts about the Equity Framework.
In an era of rampant misinformation and disinformation, what research can you trust? Dr. Stephen Gorard offers guidance!
Images contain information absent in text, and this extra information presents opportunities and challenges. It is an opportunity because one image can document variables with which text sources (newspaper articles, speeches or legislative documents) struggle or on datasets too large to feasibly code manually. Learn how to overcome the challenges.
Tips for dealing with missing data from Dr. Stephen Gorard, author of How to Make Sense of Statistics.
Learn more about standard deviation from a paper and presentation from Dr. Stephen Gorard.
This collection of open-access articles includes quantitative examples of analysis for video data.
Whether you call it ‘content analysis’, ‘textual data labeling’, ‘hand-coding’, or ‘tagging’, a lot more researchers and data science teams are starting up annotation projects these days. Learn how to avoid potential pitfalls.
Listen to Dr. Stephen Gorard discuss his no-nonsense approach to statistics.
Want to learn more about research with datasets? This curated collection of open-access articles can help you understand defining characteristics, and develop data literacy skills needed to work with large datasets and machine learning tools for managing Big Data sources.
Professor Julie Scott Jones discusses lessons learned from teaching quantitative research methods online.
After 20 years of teaching research and quantitative methods to students in Political Science in the US, UK, and the EU, Dr. Loveless has developed a teaching method that has resulted in greater student success in statistics in each passing year
Mentor in Residence Stephen Gorard explains how to use population data.


















This blog post is the eighth, and final, post in a follow-on to our 2021 “The future of computational social science is Black” series, about a Summer Institute in Computational Social Science organized by Howard University and Mathematica. It continues to bring the power of computational social science to the issues of systemic racism and inequality in America. This marks the third iteration of the successful SICSS model being hosted by a Historically Black College or University.